Applications
Used in industries such as manufacturing, food processing, chemical production, and power generation. They recover waste heat from exhaust air streams to preheat water for processes like cleaning, heating, and steam generation, without direct contact between the air and water.
Benefits
These systems improve energy efficiency by capturing and reusing waste heat, reducing fuel consumption and operational costs. Additionally, they enhance compliance with environmental regulation.
Capacities
Heat Recovery Capacity: Typically ranges from 10,000 to over 1,000,000 BTU per hour
Water Flow Rates: 10 to over 1,000 gallons per minute
Air Flow Rates: From 500 to over 100,000 cfm
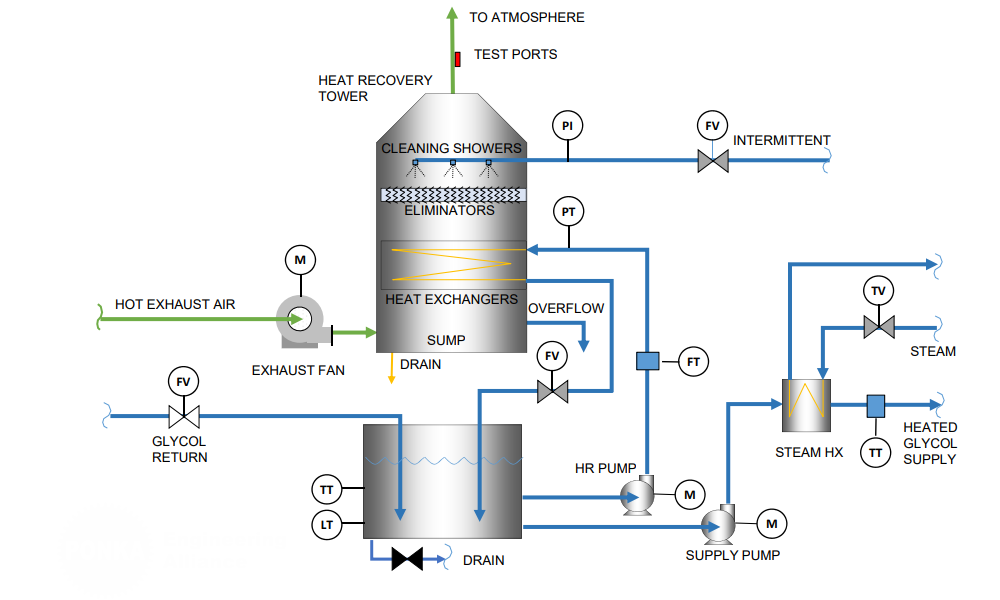
Hot exhaust air from industrial processes is directed through a heat exchanger, which consists of separate air and water channels that facilitate heat transfer without mixing the two fluids. The heat exchanger typically uses finned tubes or plate designs to maximize surface area and heat exchange efficiency. Heat from the exhaust air transfers to the water circulating in the heat exchanger, heating it up. The heated water is then stored in a reservoir or directed to processes requiring hot water, while the cooled exhaust air is vented out. Control systems regulate the flow of air and water to optimize heat recovery and maintain consistent performance.
Contact us for more information or to discuss your application and receive an estimate.
